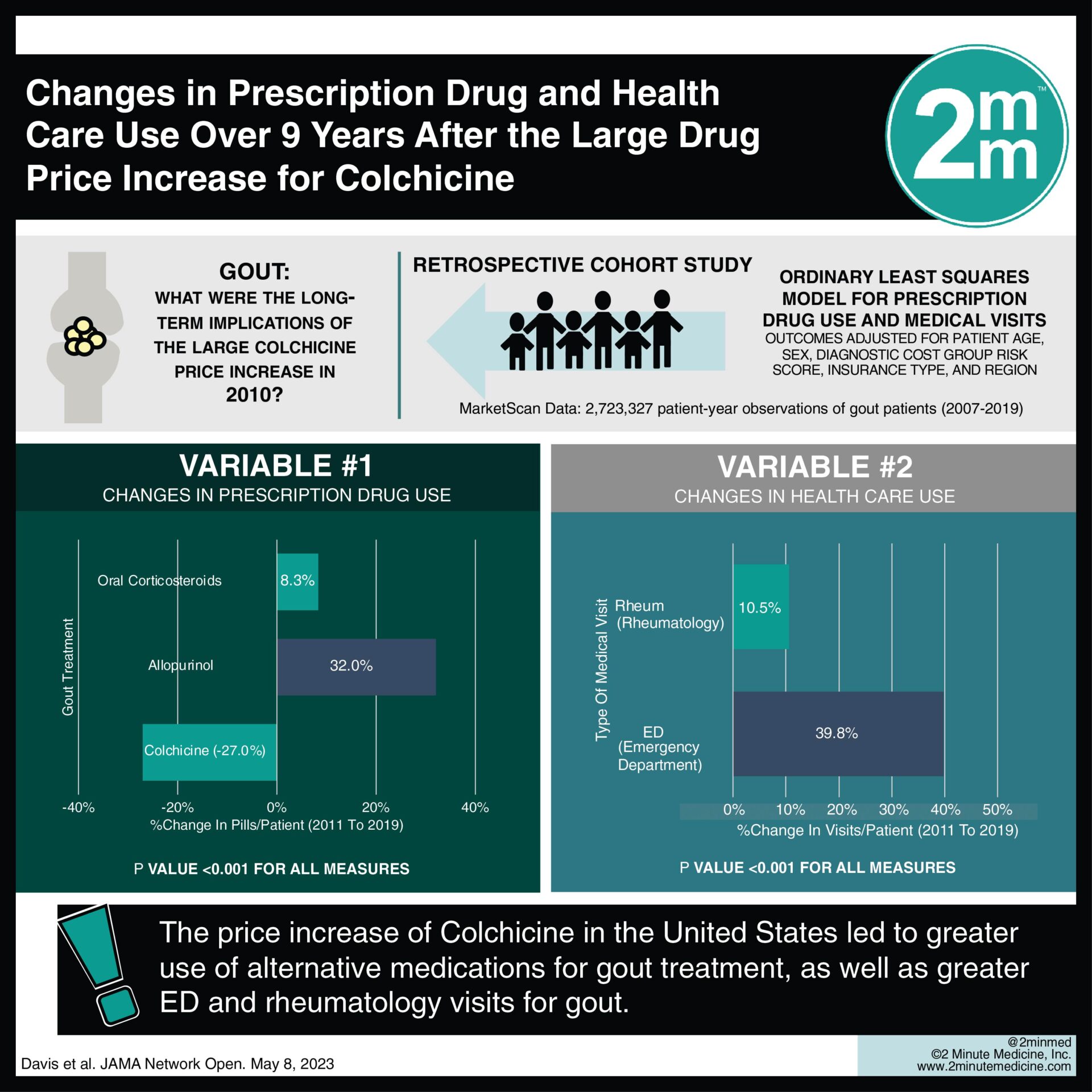
1. The price increase of Colchicine in the United States led to greater use of alternative medications for gout treatment, as well as greater ED and rheumatology visits for gout.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study rundown: Prices of prescription drugs have an important impact on the ability of patients to adhere to recommended medical treatments. The price of colchicine, a prescription medication used to treat gout, was increased in 2010 in the United States. This retrospective cohort study assessed MarketScan data from patients with gout and employer-based insurance between 2007 and 2019. The mean price of colchicine increased from $11.25 in 2009 to $190.49 in 2011, with the mean out-of-pocket cost increasing by 4.4-fold on average. The authors found that colchicine use declined following the price increase, with a 16.7% reduction in year 1 and a 27.0% reduction over the decade (p < .001). The use of allopurinol for gout treatment increased, with a 32% increase from baseline over the decade (p <0.001). Importantly, the authors found that from 2009-2019, ED visits for gout increased by 39.8% (p < .001), and rheumatology visits for gout increased by 10.5% (p <0.001). This study suggests that the cost of medications has a profound impact on medication choice, as well as the success of disease management. A limitation of this study is the exclusion of participants without employer-based insurance for drug coverage, given that this population is likely more impacted by changes to prescription medication costs.